-
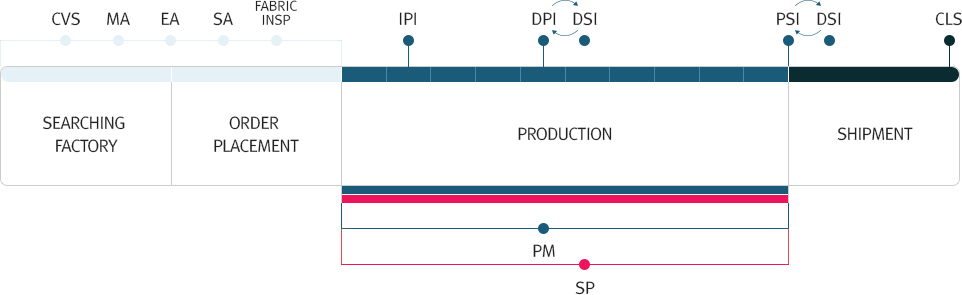
- CVS 란?
- 현지 검사원을 통해 확인하고자 하는 업체의 사업자 등록증, 조직도, 수출입 기록 등을 확인하며 해당 업체에 대한 인증작업을 하는 서비스.
- CVS 의 필요성
- 해당 회사 또는 현장에 KOTITI 검사원이 직접 방문하여 실체를 확인함과 동시에 인증서, 허가증 및 기타 서류 등의 위조를 통한 클라이언트의 피해를 미연에 방지하기 위함.
- 확인사항
-
- 사업자 등록증
- 수출업체 및 공장의 실주소
- 회사 조직도
- 대표 명함
- 근 3년간의 수출/입 내역
- 제품 및 서비스 인증서
- 유효한 은행 계좌
- 생산/조립/포장 라인
- 그 외 정보
-
- MA 란?
- 품질경영 심사(MA) 는 품질 경영 시스템을 위한 국제 표준 규격인 ISO 9000 에 기반하여 전문 심사원이 업체의 생산능력 및 QC 시스템, 시설, 작업 환경까지 모든 것을 현장에서 독립적으로 평가함. 클라이언트는 해당 업체가 요구 수준에 부합하는지 확인할 수 있음.
- MA 의 필요성
- 품질경영 심사는 비용 / 시간적 측면에서 공급업체의 프로필을 수집하는 데에 매우 효율적이고 효과적인 방법으로 클라이언트는 업체의 생산 능력, 품질 수준 등 전반적인 정보를 바탕으로 해당 업체의 신뢰도를 판단할 수 있음.
- MA 확인 사항
-
- 전문 심사원은 국제 표준 규격 ISO 9000: 2008 을 품질 경영 시스템의 표준으로 삼고 심사 시 다음의 항목을 확인함.
- 생산 능력 (범위)
- 기록 관리
- 품질 방침
- 내부 심사
- 경영 평가
- 인사 관리
- 작업 환경
- 구매
- 부적합품 관리
-
- EA 란?
- 환경심사는 환경 경영 시스템을 위한 국제표준규격인 ISO 140001 에 기반하여 전문 심사원이 해당업체가 현지 법규, 환경보호 규제에 대해 준수하여 운영되고 있는지 평가함.
- EA 의 필요성
- 클라이언트가 거래하는 공급업체 / 공장의 국제 환경 기준 및 환경 규제 규준 준수 여부를 확인하고, 환경 감사 프로그램의 포괄적인 범위에서 공급업체 / 공장의 공급사슬이 환경에 미치는 영향에 대해 모니터링하고 개선하기 위함.
- EA 확인 사항
-
- 전문 심사원은 국제 표준 규격 ISO 14001을 환경 경영 시스템의 표준으로 삼고 심사 시 다음의 항목을 확인함.
- 환경 방침
- 법적 요구조건 및 위험 평가
- 제조자 활동 관련 환경적 측면의 정의
- 환경적 목표 및 프로그램
- 소음
- 화학물질 취급 및 관리
- 폐기물 및 폐수 관리
- 대기 오염
- 자원 소모
- 에너지 대비
-
- SA 란?
- 사회적 책임 심사 (SA) 는 사회, 윤리 규준인 국제 표준 SA 8000 또는 SEDEX (SMETA) 에 기반함. 전문 심사원들은 심사 대상업체의 사회적 책임과 현지 노동법 및 기타 관련 규정 준수 여부를 독립적으로 평가함.
- SA 의 필요성
- 일부 개발도상국 공장의 경우, 노동 과부하로 인한 유소년 노동, 오염 관리 시스템의 부재, 위험한 작업 환경 등의 문제에 노출되어 있음.
사회적 책임 심사를 통해 사회 환경적 책임을 가지는 공급업체 / 공장을 선정함으로써 클라이언트는 사회적 이미지를 보호할 수 있음. - SA 확인 사항
-
- 전문 심사원은 SA 8000을 포함한 국제 규준을 따라 다음 항목을 확인함.
- 유소년 노동
- 강제 노동
- 건강 및 안전
- 단체 결사의 자유 및 단체 교섭권
- 차별
- 징계
- 작업 시간
- 보상
- 경영/관리 시스템
-
- 결점 표시 방법
-
- 10 벌점 제도(10 point system) : 면방업체, 일본 및 호주 바이어들에게 주로 사용됨. 현재 사용 정도가 감소 추세임
-
경사 방향 위사 방향 벌점 10~36 inch 반폭 초과 10 5~10 inch 5~반폭 이내 5 1~5 inch 1~5 inch 3 1 inch 이하 1 inch 이하 1 구멍, 찢어진 흠 구멍, 찢어진 흠 10 - 4 벌점 제도(4 point system) : 미국 의류제조자 협회(AAMA)와 미국 재료시험 협회(ASTM)에서 승인된 것으로 美국방성은 물론 대부분의 원단제조업체 및 의류생산업체, 바이어들에게 사용됨.
-
경,위사 방향 벌점 9 inch 이상 4 6~9 inch 3 3~6 inch 2 3 inch 이하 1
- 벌점의 산출
-
- 10 벌점 제도(10 points system)
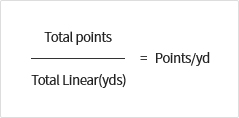
- 4 벌점 제도(4 points system)

- 합격 가능한 점수
-
- Woven Fabric
-
Fabric Types Individual Roll Shipment All Synthetic Polyester/Nylon/Acetate
Dress shirting
Filament Rayon
Worsted Spun20points/100 sq.yds.
24points/100sq.
meters16points/100sq.yds.
19points/100sq.
metersBasic Denim
Canvas
Poplin/Oxford Gingham
Shirting
Spun Rayon
Woolen Spun
Chambray/Indigo yarn dyed
All specialty fabric jacquard/Dobby
Corduroy/Velvet/Stretch denim
Cotton/Synthetic/Blends28points/100 sq.yds.
33points/100sq.
meters20points/100sq.yds.
24points/100sq.
metersLinen/Blends, Muslin, Ramie/Blends 40points/100sq.yds.
48points/100sq.
meters32points/100sq.yds.
38points/100sq.
metersDuopioni Silk/Lightweight Silk 50points/100sq.yds.
60points/100sq.
meters40points/100sq.yds.
48points/100sq.
meters - Knitted Fabric
-
Fabric Types Individual Roll Shipment All Synthetic Polyester/Nylon/Acetate
Filament Rayon
Worsted Spun
Silk Blended20points/100 sq.yds.
24points/100sq.
meters16points/100sq.yds.
19points/100sq.
metersAll specialty fabric jacquard/Dobby
Spun Rayon
Woolen Spun
Indigo yarn dyed
Velour/Spandex25points/100sq.yds.
30points/100sq.
meters20points/100sq.yds.
24points/100sq.
metersBasic Knit Fabric
(Combed Cotton/ Cotton Blended)30points/100sq.yds.
35points/100sq.
meters25points/100sq.yds.
30points/100sq.
metersBasic Knit Fabric (Carded Cotton) 40points/100sq.yds.
48points/100sq.
meters32points/100sq.yds.
38points/100sq.
meters
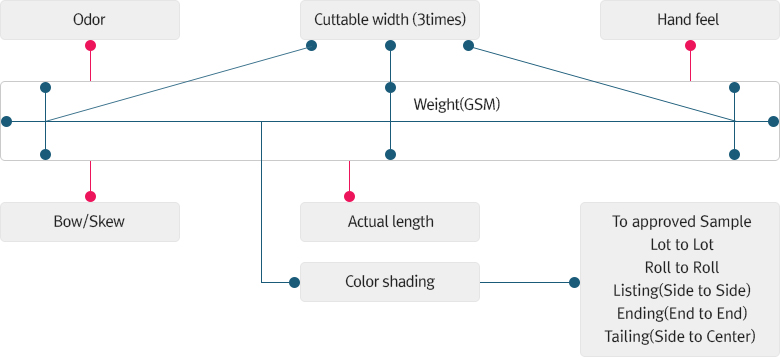
- 기타 체크 포인트
-
- PM 란?
- 생산 모니터링 (PM) 은 전문 검사원을 생산 현장에 투입하여 클라이언트와 생산업체가 초기 합의한 수준의 소재사용, 생산, 일정 등이 지켜지고 있는지 확인하는 서비스.
- PM 의 필요성
- 클라이언트는 생산업체가 사용하는 소재가 어떠한 소재인지, 요구 사항에 맞게 정확하게 생산되어지고 있는지 알 수 없기 때문에, 생산 모니터링 서비스를 통해 생산업체에 적절하고 지속적인 피드백을 줄 수 있다. 생산 모니터링을 통해 제품 생산 관련 추가적인 비용이 발생하거나 납기가 지연되는 상황을 미연에 방지할 수 있으며, 프로세스진행 상황을 수시로 확인 가능함.
- PM 확인 사항
- 검사원은 무작위로 몇 개의 제품을 선별하여 클라이언트로부터 제공받은 제품사양과 대조하면서 생산업체가 생산한 제품을 면밀히 검사한 후 수정 및 제거 해야 하는 불량유형에 대해 생산업체에 조언을 제공함. 클라이언트는 제품의 품질 및 완성 상태에 관한 1일 보고서를 수신하여 이를 통해 생산 과정 전반에 대해 컨트롤 할 수 있음.
-
- IPI 란?
- 초두 검사 (IPI)는 공장이 클라이언트의 요구사항을 이행하고 있는지 확인하고 소재, 부자재, 생산 스케줄 등 잠재적인 결점 및 문제발생을 예방하기 위함.
제품의 품질이 생산 전반에 걸쳐 일정할 수 있도록 돕는 첫 번째 단계로써 선-경고 시스템으로 제품의 세이프가드 역할을 함. - IPI 의 필요성
- 제품 생산 시 클라이언트의 요구사항을 충족하는 소재 및 부자재가 사용되는지 초기에 검사함에 따라 생산 실패 비용 및 기타 잠재적인 손해를 감소시킬 수 있음.
클라이언트의 요청으로 초두 검사 시 Sample picking 을 하여 시험을 진행하기도 함. - IPI 확인 사항
-
- 모든 검사 시, 검사원은 국제 표준 규격인 ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 (ISO 2859-1) 계수형 샘플링 절차를 표준으로 하여 검사를 진행함.
초두 검사 시 다음과 같은 전반적인 부분을 검사 함. - 봉제작업 상태
- 기능
- 제품 외관 전반
- 내구성
- 치수
- 모든 검사 시, 검사원은 국제 표준 규격인 ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 (ISO 2859-1) 계수형 샘플링 절차를 표준으로 하여 검사를 진행함.
-
- DPI 란?
- 중간 검사 (DPI) 는 오더 수량의 40-50% 정도가 생산-선적포장까지 완료되었을 때 수행됨. 이 검사는 현장 검사로서 검사원이 제품을 무작위로 제품을 선별하여 PO, 작업지시상의 스펙 충족 여부 확인 및 초두검사에서 발생한 이슈가 올바르게 수정되었는지 확인하고 제공된 기준과 상이한 부분 및 외관결점에 대한 정보를 클라이언트에게 제공함.
- DPI 의 필요성
- 클라이언트는 검사원이 상세히 확인한 생산진행 상태, 생산공정, 생산일정, 제품품질 상태 등의 정보를 가지고 초기 제조 공정 및 제품에서 발견된 이슈에 대해 초기단계에 대응 하여 추후에 발생할 수 있는 더 큰 문제에 대해 예방할 수 있음.
- DPI 확인 사항
-
- 모든 검사 시, 검사원은 국제 표준 규격인 ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 (ISO 2859-1) 계수형 샘플링 절차를 표준으로 하여 검사를 진행함.
중간 검사 시 다음과 같은 전반적인 부분을 검사 함. - 봉제작업 상태
- 기능
- 제품 외관 전반
- 내구성
- 치수
- 모든 검사 시, 검사원은 국제 표준 규격인 ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 (ISO 2859-1) 계수형 샘플링 절차를 표준으로 하여 검사를 진행함.
-
- PSI 란?
- 선적 전 검사 (PSI) 는 오더수량의 100% 생산 완료, 선적포장상태가 최소 80% 이상 완료된 시점에서 수행됨.
준비된 제품 중 무작위로 제품을 발췌하여 체계적인 검사를 진행함. 패킹상태부터 사이즈, 제품 외관, 현장기능 검사 등 마지막 검사 단계인 만큼 상세한 검사가 이루어짐. - PSI 의 필요성
- 이 시점은 클라이언트가 교정 액션을 취할 수 있는 마지막 기회로 막대한 비용이 드는 수입 리스크를 감소시키는 효율적인 안전책이며 저품질 제품이 시장 및 고객에게 전달되는 위험을 감소 시킬 수 있음. 클라이언트는 저품질 제품에 대한 소비자의 컴플레인을 예방 할 수 있으며 동시에 브랜드 이미지를 유지할 수 있음. 또한 클라이언트가 상시 공장 및 제품에 대한 관리 / 감독을 실시하고 있다는 것을 공장이 인지하게끔 하여 결과적으로 제품의 품질 수준이 높게 유지되고 납기가 지연 되지 않도록 함.
- PSI 확인 사항
-
- 모든 검사 시, 검사원은 국제 표준 규격인 ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 (ISO 2859-1) 계수형 샘플링 절차를 표준으로 하여 검사를 진행함.
선적 전 검사 시 다음과 같은 전반적인 부분을 검사 함. - 수량
- 포장 상태
- 선적표기
- 라벨, 로고, 행택
- 제품 외관 전반
- 치수 측정
- 현장기능검사(ON-SITE TEST)
- 모든 검사 시, 검사원은 국제 표준 규격인 ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 (ISO 2859-1) 계수형 샘플링 절차를 표준으로 하여 검사를 진행함.
-
- DSI 란?
- 부적합품 선별 검사는 특정적인 외관불량, 기능 불량 또는 포장 미흡 등과 같은 문제를 가진 제품들에서 정해진 일정 기간 동안 가능한 많은 해당 불량제품을 선별하는 검사이며 처음 대두되었던 문제 이외에 다른 부분은 검사 진행 하지 않음
- DSI 의 필요성
- 클라이언트의 기준에 따라 재작업된 제품에 대한 불량률을 체크할 수 있는 효율적인 방법으로 이 검사를 통해 공장이 클라이언트의 요구조건에 따라 올바르게 재작업을 했는지, 하고 있는지 확인할 수 있음. 또한 클라이언트와 공급자 간의 거래 후 제품에 문제 발생 시 부적합품 선별 검사를 진행 함으로써 정확하고 공정하게 문제 상태를 확인할 수 있음
- DSI 확인 사항
-
- 수량
- 외관 결점
- 기능 결함
- 죽거나 살아있는 곤충
- 악취
- 부러진 바늘, 금속
- 그 외
-
- SP 란?
- 샘플 채취 (SP) 는 클라이언트를 대신하여 현지검사원이 공장을 방문하여 무작위로 샘플을 채취하고, 이를 클라이언트에게 직접 발송하거나 클라이언트가 지정한 시험실에 전달하는 서비스
- SP 의 필요성
- 공급자에 의해 제공된 샘플제품의 품질이 클라이언트가 제시한 기준에 충족되지 않는다고 판단될 경우 샘플픽킹 서비스를 통해 제품의 품질상태를 정확히 판단할 수 있음. 클라이언트가 거리/시간상 공장을 직접 방문하는데 제약이 있는 경우 현지 검사원을 활용함으로써 시간, 비용 면에서 효율적임.
- SP 확인 사항
- 검사원은 클라이언트의 요청에 따라 무작위로 샘플을 채취함. 채취된 샘플은 채취 전용 포장 비닐에 넣고 봉한 후 패키지 겉면에 품명, 품번, 색상 등을 적고 검사원 서명을 한 후 증거로 사진촬영을 함. 이 사진은 SP 검사보고서에 첨부됨.
-
- CLS 란?
- 선적 감독 검사 (CLS) 는 PSI(선적 전 검사) 까지 완료 후 최종 단계에서 수행됨. 전문검사원은 선적 대상인 CARTON에 대해 수량, 패킹 상태, 패킹재질, 라벨, 마킹 및 담고 있는 제품의 사양이 클라이언트의 요구사항과 부합하는지에 대해 확인함.
이때 개봉되는 CARTON은 적어도 품번, 색상 별 1 개씩은 포함되도록 함 - CLS 의 필요성
- 선적 감독 검사(CLS)는 제품의 최종 상태가 클라이언트의 요구조건에 부합하는지, 실제 주문 수량이 컨테이너에 안전하게 선적되는지를 최종 승인 및 대금 지불 전에 확인하는 서비스로써 이 검사를 통해 클라이언트는 지정한 목적지에 부정확한 수량의 제품이 선적되거나 손상된 제품이 전달되는 위험을 최소화할 수 있음. 또한 제품이 선적되는 동안 수행되는 현장 확인 작업은 공급 업체에게 클라이언트가 상시 프로세스를 관리 / 감독 중이라는 메시지를 전달하여 공급 체인을 관리함에 있어 긍정적 효과를 기대할 수 있음.
- CLS 확인 사항
-
- 수량
- 패킹리스트
- CARTON 포장 상태
- 개별 포장 상태
- 컨테이너 내부/외부상태
- 제품 스펙
- 화인
- 라벨
- SEAL, 컨테이너 번호